Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is strategic management?
Strategic management is defined as the dynamic process of formulation, implementation, evaluation and control of strategies to realize the organization’s strategic intent.
First, strategic management is a dynamic process. It is not a one-time, static or mechanistic process. By being dynamic, strategic management is a continual, evolving, iterative process. By this, it means that strategic management cannot be a rigid, step-wise collection of a few activities arranged in a sequential order.
Rather, it is a continually evolving mosaic of relevant activities. Managers perform these activities in any order contingent upon the situation they face at a particular time.
By being iterative, an activity may not be required to be performed only once but repeated over time as the situation demands.
Characteristics of Strategic management:
They are:
- Uncertain : Strategic management deals with future-oriented non-routine situation. They create uncertainly. Managers are unaware about the consequences of their decisions.
- Complex : Uncertainly brings complexity for strategic management. Managers face environment which is difficult to comprehend. External and internal environment is analysed.
- Organization wide : Strategic management has organization wide implication. It is not operation specific. It is a systems approach. It involves strategic choice.
- Fundamental : Strategic management is fundamental for improving the long-term performance of the organization.
- Long-term implication : Strategic management is not concerned with day-to-day operation.It has long-term implications.It deal with vision,mission and objective.
- Implication : Strategic management ensure that strategic is put into action,implementation is done through action plans.
Strategic management is important due to following reasons:
- Participative management : Strategic management involves interaction at all levels of organization. It promotes participant management .It empowers employees.
- Problem prevention: Strategic management enhances problem prevention capabilities of the organization. Problems anticipated and addressed during strategy formulation stage. This facilities problem presentation during strategy implementation.
- Better options : Group interaction generated better strategic options at alternatives for strategic choice.
- Motivation : Employees are motivation by performances reward relationship .This improves productivity and goal directed behaviour.
- Reduced gaps and overlaps : Strategic management takes an integrated approach to resources allocation. This reduces gapes and overlaps in activities .Rules and responsibilities are clearly specified. Strategic fit facilitates effective resources utilization.
- Change management : Strategic management reduces Resistance to change.The participative approach promotes participation and communication .Uncertainly is reduced.Strategic change is facilitated.
- Financial benefit : Strategic management leads to higher profitability.
Phases in the strategic management process
The next part of the definition states the four phases in the strategic management process of formulation, implementation and evaluation and control. The four phases are shown in Exhibit below
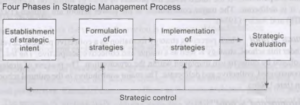
The first phase consists of establishing the strategic intent for the organisation.
In this text, strategic intent is the hierarchy of objectives that an organisation sets for itself. Within this, there are the vision, mission, business definition and objectives. The aim of strategic management is to help the organisation realise its strategic intent.
The second phase of the formulation of strategies is concerned with the devising of a strategy or a few strategies. This phase is also called strategic planning. Essentially, this is an analytical phase in which strategists (managers who are responsible for strategic management in an organisation) think, analyse and plan strategies.
The third phase of implementation is the ‘putting into action’ phase. The strategies that are formulated are implemented through a series of administrative and managerial actions.
The fourth and the last phase of evaluation and control involves assessing how appropriately the strategies were formulated and how effectively they are being implemented. Depending on the outcome of assessment, actions could be taken ranging from fine-tuning implementation to a drastic reformulation of strategies.
These four phases are considered to be sequentially linked to each other and each successive phase provides a feedback to the previous phases. However, in practice, the different phases of strategic management may not be clearly differentiable from each other. In fact, we prefer to call them phases rather than stages or steps (as some authors do) to signify that the different phases, at the interface, may exist simultaneously and the strategic activities gradually emerge in one phase to merge into the following phase.
The feedback arising from each of the successive phases is meant to revise, reformulate or redefine the previous phases, if necessary. Such a representation yields a dynamic model of strategic management which takes into account the emerging factors as the process moves on.
Elements in Strategic Management Process
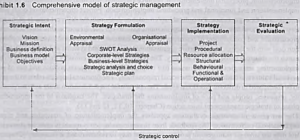
Each phase of the strategic management process consists of a number of elements, which are discrete and identifiable activities performed in logical and sequential steps. As many as twenty different elements could be identified in the models provided by various authors.
From the literature on strategic management, we note that most or all of the following activities are considered as parts of the strategic management process:
- Establishing the hierarchy of strategic intent:
- Creating and communicating a vision
- Designing a mission statement
- Defining the business
- Adopting the business model
- Setting objectives
- Formulation of strategies:
-6. Performing environmental appraisal
7.doing organisational appraisal
- Formulating corporate – level strategies
- formulating business-level strategies
- undertaking strategic analysis
- Exercising strategic choice
- Preparing strategic plan
- implementation of strategies:
- Activating strategies
- Designing the structure, systems and processes
- Managing behavioural implementation
- Managing functional implementation
- Operationalising strategies
- Performing strategic evaluation and control:
- Performing strategic evaluation
- Exercising strategic control
- Reformulating strategies
Bird’s-eye view of the different elements of the process.
The hierarchy of strategic intent
lays the foundation for the strategic management of any organisation. In this hierarchy, the vision, mission, business definition, business model and objectives are established.
The strategic intent makes clear what the organisation stands for. The element of vision in the hierarchy of strategic intent serves the purpose of stating what the organisation wishes to achieve in the long run.
The mission relates the organisation to the society. The business definition explains the businesses of the organisation in terms of customer needs, customer groups and alternative technologies.
The business model clarifies how the organisation creates revenue. The objectives of the organisation state what is to be achieved in a given time period. These objectives then serve as yardsticks and benchmarks for measuring organisational performance .
Environmental and organisational appraisal
deal with identifying the opportunities and threats operating in the environment and the strengths and weaknesses of the organisation in order to create a match between them in such a manner that opportunities could be availed of and the impact of threats neutralised and to capitalise on the organisational strengths and minimise the weaknesses .
Formulation of strategies
takes place at four levels: corporate, business, functional and operational.
Among these levels, the major ones are the corporate and business level strategies.
Corporate level strategies relate to the strategic decisions regarding the management of a portfolio of businesses.
Business strategies aim at developing a competitive advantage in the individual businesses that a company has in its portfolio.
Strategic alternatives and choice
are required for evolving alternative strategies, out of the many possible options and choosing the most appropriate strategy or strategies in the light of environmental opportunities and threats and corporate strengths and weaknesses. Strategies are chosen at the corporate-level and the business-level. The process used for choosing strategies involves strategic analysis and choice. The end result of this set of elements is a strategic plan to be implemented .
implementation of strategy,
the strategic plan is put into action through six sub-processes: project implementation, procedural implementation, resource allocation, structural implementation, behavioural implementation and functional and procedural implementation. Project implementation deals with the setting up of the organisation. Procedural implementation deals with the different aspects of the regulatory framework within which Indian organisations have to operate. Resource allocation relates to the procurement and commitment of resources for implementation. The structural aspects of implementation deal with the design of appropriate organisational structures and systems and reorganising so as to match the structure to the needs of strategy. The behavioural aspects consider the leadership styles for implementing strategies and other issues like corporate culture, corporate politics and use of power,personal values and business ethics and social responsibility. The functional aspects relate to the policies to be formulated in different functional areas. The operational implementation deals with the productivity, processes, people and pace of implementing the strategies. The emphasis in the implementation phase of strategic management is on action.
strategic evaluation
The last phase of strategic evaluation appraises the implementation of strategies and measures organisational performance. The feedback from strategic evaluation is meant to exercise strategic control over the strategic management process. Strategies may be reformulated, if necessary.
