SWOT ANALYSIS – A STRATEGIC TOOL
SWOT Analysis
A scan of the internal and external environment is an important part of the strategic planning process. Environmental factors internal to the firm usually can be classified as strengths (S) or weaknesses (W), and those external to the firm can be classified as opportunities (O) or threats (T). Such an analysis of the strategic environment is referred to as a SWOT analysis.
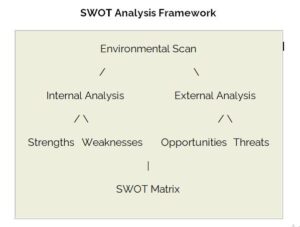
The SWOT analysis provides information that is helpful in matching the firm’s resources and capabilities to the competitive environment in which it operates. As such, it is instrumental in strategy formulation and selection. The following diagram shows how a SWOT analysis fits into an environmental scan:
SWOT Analysis Framework
Strengths
A firm’s strengths are its resources and capabilities that can be used as a basis for developing a competitive advantage. Examples of such strengths include:
- patents
- strong brand names
- good reputation among customers
- cost advantages from proprietary know-how
- exclusive access to high grade natural resources
- favorable access to distribution networks
Weaknesses
The absence of certain strengths may be viewed as a weakness. For example, each of the following may be considered weaknesses:
- lack of patent protection
- a weak brand name
- poor reputation among customers
- high cost structure
- lack of access to the best natural resources
- lack of access to key distribution channels
In some cases, a weakness may be the flip side of a strength. Take the case in which a firm has a large amount of manufacturing capacity. While this capacity may be considered a strength that competitors do not share, it also may be a considered a weakness if the large investment in manufacturing capacity prevents the firm from reacting quickly to changes in the strategic environment.
Opportunities
The external environmental analysis may reveal certain new opportunities for profit and growth. Some examples of such opportunities include:
- an unfulfilled customer need
- arrival of new technologies
- loosening of regulations
- removal of international trade barriers
Threats
Changes in the external environmental also may present threats to the firm. Some examples of such threats include:
- shifts in consumer tastes away from the firm’s products
- emergence of substitute products
- new regulations
- increased trade barriers
The SWOT Matrix
A firm should not necessarily pursue the more lucrative opportunities. Rather, it may have a better chance at developing a competitive advantage by identifying a fit between the firm’s strengths and upcoming opportunities. In some cases, the firm can overcome a weakness in order to prepare itself to pursue a compelling opportunity.
To develop strategies that take into account the SWOT profile, a matrix of these factors can be constructed. The SWOT matrix (also known as a TOWS Matrix) is shown below: \
SWOT / TOWS Matrix
| Strengths | Weaknesses | |
| Opportunities | S-O strategies | W-O strategies |
| Threats | S-T strategies | W-T strategies |
- S-O strategies pursue opportunities that are a good fit to the company’s strengths.
- W-O strategies overcome weaknesses to pursue opportunities.
- S-T strategies identify ways that the firm can use its strengths to reduce its vulnerability to external threats.
- W-T strategies establish a defensive plan to prevent the firm’s weaknesses from making it highly susceptible to external threats.
The environment in which an organization exists can, therefore, be described in terms of the strengths and weakness existing in the internal environment and the opportunities and threats operating in the external environment.
The four environmental influences could be described as below.
Internal environment:
- Strength is an inherent capacity which an organisation can use to gain strategic advantage.
Examples of strength are: good reputation among customers, resources, assets, people, experience, knowledge, data and capabilities. Good reputation ,• Excellent distribution network • Established research and development unit • Strong advertising • High product demand ‘
- Weakness is an inherent limitation or constraint which creates strategic disadvantages.
Examples of weakness are: gaps in capabilities, financial deadlines, low morale and overdependence on a single product line. • High Employee Turnover• Uncertain cash flow• Weak Product demand• Inadequate resources • Old technology
External environment:
- Opportunity is a favorable condition in the organisation’s environment which enables it to consolidate and strengthen its position.
Examples of opportunity are: economic boom, favourable demographic shifts, arrival of new technologies, loosening of regulations, favourable global influences and unfulfilled customer needs. • Favorable industry trends • Emergence of new markets • Availability of low cost technology • Favorable government laws
- Threat is an unfavourable condition in the organisation’s environment which creates a risk for, or causes damage to, the organisation.
Examples of threat are: economic downturn, demographic shifts, new competitors, unexpected shifts in consumer tastes, demanding new regulations, unfavourable political or legislation, new technology and loss of key staff. • Unfavorable political environment• Entry of new competitors• New competitor strategies • Strict regulations by the government
