Michael porter’s generic business strategies
Michael Porter has called business-level strategies as generic business strategies. Porter defined each generic strategy with the help of two dimensions, which are as follows:
- Competitive Advantage: Implies the supply-side dimension that focuses on the competitiveness and strength of the organization
- Competitive Scope: Refers to a demand-side dimension that focuses on the size and composition of the target market.
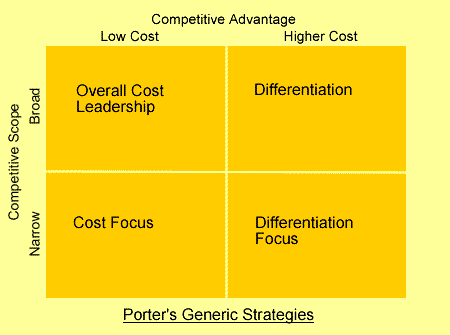
1.Cost Leadership:
- Refers to a strategy in which an organization produces products at the lowest cost.
- An organization can gain competitive advantage as a cost leader in the market by producing standardized products in high volumes. This helps the organization to gain economies of scale or efficiency.
- An organization needs to continuously search for low cost factors of production to achieve and maintain this strategy.
- The sole aim of cost leadership strategy is cost reduction in the production of basic products for a wide range of customers.
2. Differentiation:
- Refers to a strategy in which an organization offers differentiated products in the market to attain competitive advantage.
- Unlike the cost leadership strategy, where the focus is on cost control, this strategy completely focuses on giving customized products to its customers to satisfy their needs.
- Differentiation strategy allows organizations to focus on value creation of the product, which in turn allows them to charge premium prices.
- Value is provided to customers through unique features and characteristics of an organization’s products rather than by the lowest price.
- This is done through high quality, features, high customer service, rapid product innovation, advanced technological features, image management, etc. (Some companies that follow this strategy: Rolex, Intel, Ralph Lauren)
- In addition, the organization is required to segment the target market in such a way that it targets the products and services in a profitable manner.
- Market segmentation can be done by differentiation of products in terms of design, brand image, technology, features, dealers, network, or customer’s service.
Focus Strategy:
Focus Strategy: Concentrates on selecting a specific customer segment with a view to cater to its specific needs by customizing the marketing mix and product mix. Markets entailing very specific customer segments are called niche markets.
The focus strategy is suitable for the smaller organizations that neither have cost leadership nor differentiation strategy. It allows organizations to streamline their efforts and resources on a narrow and specifically defined segment of a market. Every market segment or niche has its own competitive advantage.
Organizations can use the two variants of focus strategy, namely:
-
Focused Low Cost leadership–
Opts for the strategy that focuses on cost reduction. Focused cost strategy is adopted by organizations that sell products at low cost in small markets.
Organizations not only compete on price, but also select a small segment of the market to provide goods and services to. For example a company that sells only to the U.S. government.
-
Focused Differentiation–
Organizations not only compete based on differentiation, but also select a small segment of the market to provide goods and services.
Focused Strategies – Strategies that seek to serve the needs of a particular customer segment (e.g., federal gov’t).
