Organizational culture is the collection of values, expectations, and practices that guide and inform the actions of all team members. Think of it as the collection of traits that make your company what it is. A great culture exemplifies positive traits that lead to improved performance, while a dysfunctional company culture brings out qualities that can hinder even the most successful organization.
Organisational culture defines the way employees complete tasks and interact with each other in an organization. The cultural paradigm comprises various beliefs, values, rituals and symbols that govern the operating style of the people within a company. Corporate culture binds the workforce together and provides a direction for the company. In times of change, the biggest challenge for any organization may be to change its culture, as the employees are already accustomed to a certain way of doing things.
The dominant culture in organizations depends on the environment in which the company operates, the organization’s objectives, the belief system of the employees and the company’s management style.
Therefore, there are many organizational cultures.
Bureaucratic Culture
For example, highly bureaucratic and well-structured organizations typically follow a culture with extensive controls. Employees follow standard procedures with a strict adherence to hierarchy and well-defined individual roles and responsibilities.
Competitive Culture
Those in competitive environments, such as sales, may forgo strict hierarchies and follow a where the focus is on maintaining strong competitive culture relationships with external parties. In this instance, the strategy is to attain competitive advantages over the competition.
collaborative culture
The collaborative culture is yet another organizational way of life. This presents a decentralized workforce with integrated units working together to find solutions to problems.
Strong corporate cultures indicate that employees are like-minded and hold similar beliefs and ethical values. When these beliefs and ethical values align with business objectives, they can prove to be effective in building teams because rapport and trust quickly ensue. The bonds that the teams build help them avoid conflicts and focus on task completion. Strong corporate cultures ease communication of roles and responsibilities to all individuals. Employees know what is expected of them, how management assesses their performance and what forms of rewards are available.
Effect on Performance
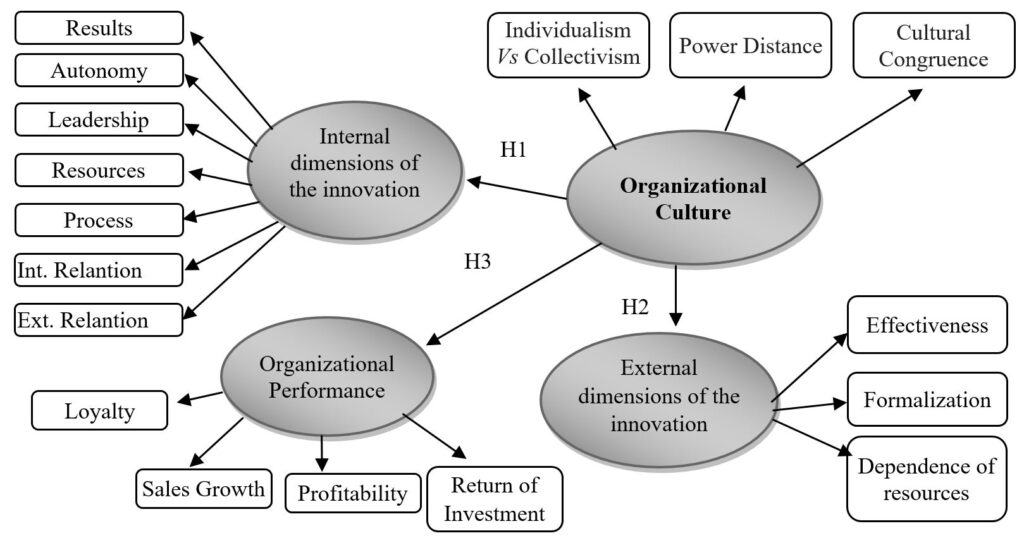
Organizational cultures can have varying impacts on employee performance and motivation levels. Oftentimes, employees work harder to achieve organizational goals if they consider themselves to be part of the corporate environment. Different cultures operating in one company can also impact employee performance. For example, if the organization maintains a reserved “talk when necessary” culture, employees may work accordingly; however, if the organization allows one area, say the sales team, to be outspoken and socially active, the organization may experience rivalries among areas. Thus, allowing an area to set up their own culture can affect the performance of the employees deployed elsewhere in the company.
Integration of Performance and Culture
Organizations must structure their recruitment processes to attract and engage incumbents with the same beliefs and values that constitute the organization’s culture. This ensures the new employee’s assimilation to the company and further strengthens corporate culture. Companies should also ensure that they align corporate culture with performance management systems. When culture and management systems are not aligned, management must redirect them so that employee behaviour results in the achievement of organizational goals.
