Concept of National Income
National income
Income: The amount of money or its equivalent received during a period of time in exchange for labor or services, from the sale of goods or property, or as profit from financial investments.
The amount of monetary or other returns, either earned or unearned, accruing over a given period of time
Net income is calculated by taking revenues and adjusting for the cost of doing business, depreciation, interest, taxes and other expenses.
Net income represents the amount of money remaining after all operating expenses, interest, taxes and preferred stock dividends (but not common stock dividends) have been deducted from a company’s total revenue.
Difference between income and profit
Income means revenue, which is sales or other income through earning , interest, etc. Profit is the positive number you get from subtracting your expenses from your income (revenue)
National income:
National income is the total value a country’s final output of all new goods and services produced in one year. Understanding how national income is created is the starting point for macroeconomics.
Factor cost: the cost of an item of goods or a service in terms of the various factors which have played a part in its production or availability, and exclusive of tax costs.
Alfred Marshall in his ‘Principle of Economics’ (1949) defines National income as
“The labour and capital of a country, acting on its natural resources, produce annually a certain net aggregate of commodities, material and immaterial, including services of all kinds…..and net income due on account of foreign investments must be added in. This is the true net National income or Revenue of the country or the national dividend.”
Central Statistical Organization defines National income as
“National Income is the sum of factor income earned by the normal residents of a country in the form of wages, rent, interest and profit in an accounting year.”
The Importance of National Income
Measuring national income is crucial for various purposes:
- The measurement of the size of the economy and level of country’s economic performance;
- To trace the trend or the speed of the economic growth in relation to previous year(s) also in other countries;
- To know the composition and structure of the national income in terms of various sectors and the periodical variations in them.
- To make projections about the future development trend of the economy.
- To help government formulate suitable development plans and policies to increase growth rates.
- To fix various development targets for different sectors of the economy on the basis of the earlier performance.
- To help businesses to forecast future demand for their products.
- To make international comparison of people’s living standards.
- National income is the sum total of all the incomes earned by a nation during a particular period of time.
- National income shows how the income is distributed between the wages, interest, profit and rents.
- National income is treated as an index of the economic activity of a nation. If national income reduces, the government will cut down the taxes so that citizens will have more income to spend.
Concepts of National Income
There are different concepts of National Income, namely; GNP, GDP, NNP, Personal Income and Disposable Income.
Gross Domestic Product
- GDP is commonly used as an indicator of the economic health of a country, as well as to gauge a country’s standard of living.
- GDP, is one of the ways of measuring the size of its economy.
- The GDP of a country is defined as the total market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time (usually a calendar year).
- Critics of using GDP as an economic measure say the statistic does not take into account the underground economy – transactions that, for whatever reason, are not reported to the government.
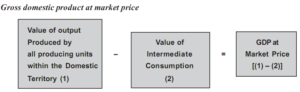
GDP at market price ( Product method)
GDP at Market Price is estimated by deducting the value of intermediate consumption from the value of output produced by all the producers within the domestic territory of a country.
In other words, it is estimated as the sum total of gross value added at the market price.
Final goods here refer to those goods which are directly consumed and not used in further production process.
Goods which are further used in production process are called intermediate goods. In the value of final goods, value of intermediate goods is already included therefore we do not count value of intermediate goods in national income otherwise there will be double counting of value of goods.
How to calculate GDP- Expenditure method
The method of Calculating India GDP is the expenditure method, which is,
GDP = consumption + investment + (government spending) + (exports-imports)
and the formula is GDP = C + I + G + (X-M)
Where,
C stands for consumption which includes personal expenditures pertaining to food, households, medical expenses, rent, etc
I stands for business investment as capital which includes construction of a new mine, purchase of machinery and equipment for a factory, purchase of software, expenditure on new houses, buying goods and services but investments on financial products is not included as it falls under savings
G stands for the total government expenditures on final goods and services which includes investment expenditure by the government, purchase of weapons for the military, and salaries of public servants
X stands for gross exports which includes all goods and services produced for overseas consumption
M stands for gross imports which includes any goods or services imported for consumption and it should be deducted to prevent from calculating foreign supply as domestic supply
Points to remember while calculating GDP
- Calculating India GDP has to be done cautiously pertaining to the diversity of the Indian Economy.
- There are different sectors contributing to the GDP in India such as agriculture, textile, manufacturing, information technology, telecommunication, petroleum, etc.
- The different sectors contributing to the India GDP are classified into three segments, such as primary or agriculture sector, secondary sector or manufacturing sector, and tertiary or service sector.
- With the introduction of the digital era, Indian economy has huge scopes in the future to become one of the leading economies in the world.
- India has become one of the most favored destinations for outsourcing activities.
- India at present is one of the biggest exporter of highly skilled labor to different countries
- The new sectors such as pharmaceuticals, nanotechnology, biotechnology, telecommunication, aviation, manufacturing, shipbuilding, and tourism would experience very high rate of growth
Gross National Product (GNP)
GNP at market price is sum total of all the goods and services produced in a country during a year and net income from abroad.
GNP is the sum of Gross Domestic Product at Market Price and Net Factor Income from abroad.

Factor incomes: There are generally four factors of production labour, capital, land and entrepreneurship. Labour gets wages and salaries, capital gets interest, land gets rent and entrepreneurship gets profit as their remuneration.
Net factor income:
While calculating GNP, the final goods and services of the following are considered:
(a) Consumer goods and services.
(b) Gross private domestic income.
(c) Goods and services produced by Governm he general formula used for Gross National Product is:
GNP = GDP + Net factor income from abroad
Where, GDP = Gross Domestic Product
Net factor income from abroad = income earned in foreign countries by the residents of a country – income earned by non-residents in that country
Why is GNP required?
The Gross National Product is helpful in measuring the contribution of a country’s residents to the flow of goods and services inside and outside the national territory. Therefore, Gross National Product is the basic concept of national income accounting.
Measurement of GNP
The GNP is measured at:
- Current market prices (Nominal GNP)
This method of estimating the GNP involves measuring the GNP at the prices of goods and services being measured at the prices existing in the market in current year.
- Constant prices (Real GNP)
Through this method, Gross National Product is estimated at a fixed price of a specific base year.
(d) Net income from abroad.
Net National Product (NNP)
In the process of production of goods and services, there will be some depreciation of fixed capital also called as consumption of fixed capital, if the value of depreciation is deducted from the value of gross national product in a year, we obtain the value of net national product.
Thus, NNP at market price is gross national product at market price minus depreciation.

Private income : Private income is obtained by private individuals from any source productive or otherwise and the retained income of corporations.
Personal income : Personal income is the total income received by the individuals of a country from all source prior to direct taxes in one year.
Disposable income: Disposable income or personal disposable income refers to the actual income which can be spent on consumption by individuals and families.
Real income Real income is nothing but the national income expressed in terms of a general level of prices of a particular year which is taken as base year.
Percapita Income:
The average income of the people of a country in a particular year is called percapita income for that year. Percapita Income is derived from dividing national income from the total population of the country.
PCI = NI/ Population
Methods of national income:
The national income of a country can be measured by three alternative methods: (i) Product Method (ii) Income Method, and (iii) Expenditure Method.
- Product Method:
In this method, national income is measured as a flow of goods and services. We calculate money value of all final goods and services produced in an economy during a year. Final goods here refer to those goods which are directly consumed and not used in further production process.
Goods which are further used in production process are called intermediate goods. In the value of final goods, value of intermediate goods is already included therefore we do not count value of intermediate goods in national income otherwise there will be double counting of value of goods.
To avoid the problem of double counting we can use the value-addition method in which not the whole value of a commodity but value-addition (i.e. value of final good value of intermediate good) at each stage of production is calculated and these are summed up to arrive at GDP.
The money value is calculated at market prices so sum-total is the GDP at market prices. GDP at market price can be converted into by methods discussed earlier.
- Income Method:
Under this method, national income is measured as a flow of factor incomes. There are generally four factors of production labour, capital, land and entrepreneurship. Labour gets wages and salaries, capital gets interest, land gets rent and entrepreneurship gets profit as their remuneration.
Besides, there are some self-employed persons who employ their own labour and capital such as doctors, advocates, CAs, etc. Their income is called mixed income. The sum-total of all these factor incomes is called NDP at factor costs.
- Expenditure Method:
In this method, national income is measured as a flow of expenditure. GDP is sum-total of private consumption expenditure. Government consumption expenditure, gross capital formation (Government and private) and net exports (Export-Import).
